Given that,
- $ 2x^{2} – ax + 2 > 0 \quad \longrightarrow (1) $
- $ x^{2} – bx + 8 \geqslant 0 \quad \longrightarrow (2) $
For any quadratic equation $ax^{2} + bx + c > 0 $
If $a$ is greater than zero then this means that the quadratic equation will always be above $x\text{-axis}$ and will never intersect it at any real value of $x.$ Thus the solutions to this equation will be imaginary.
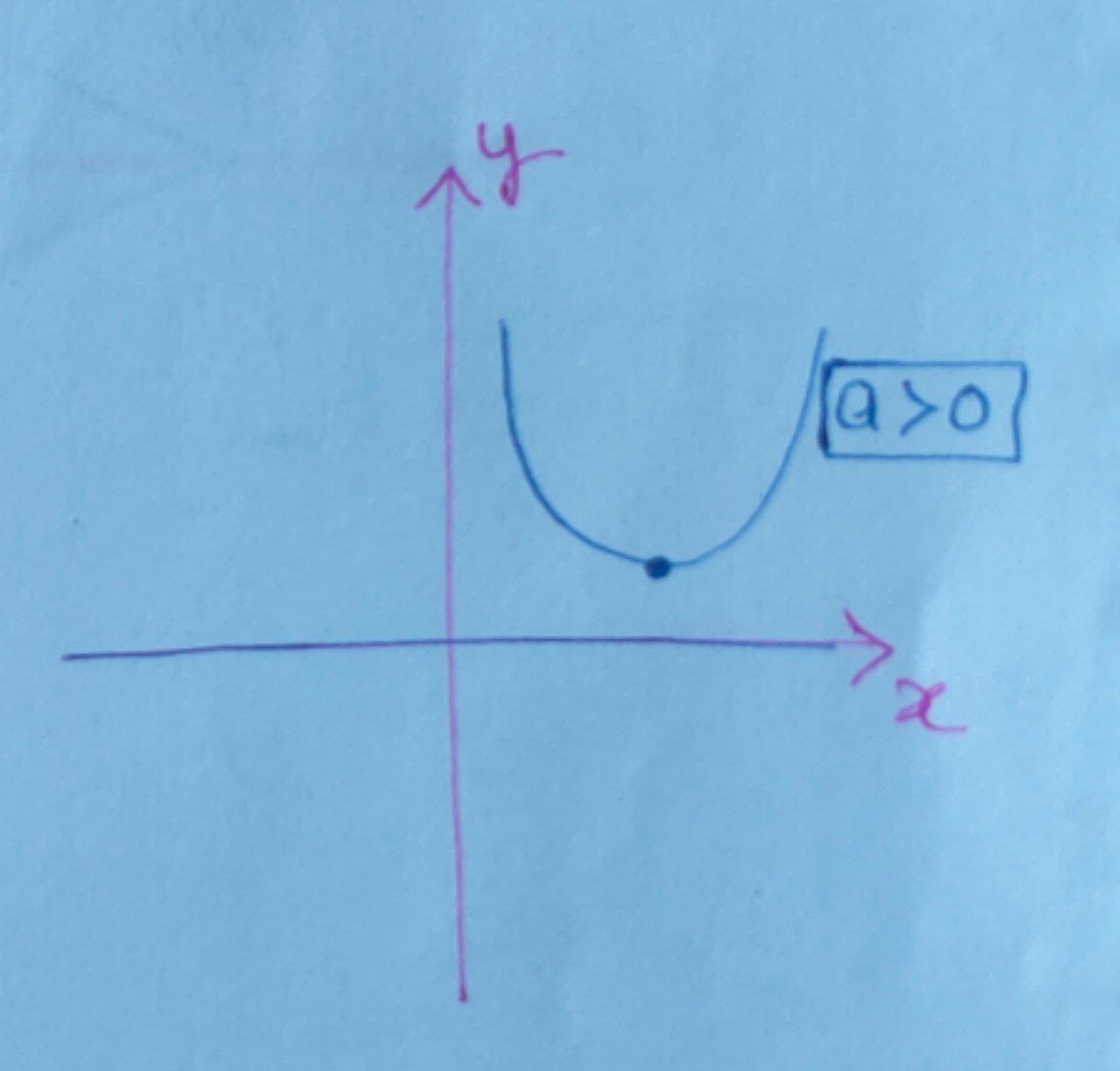
So, here discriminant $\boxed{\text{D<0}}$
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{ b^{2} – 4ac < 0} $
On the other hand for an inequality $ ax^{2} + bx + c < 0 $ for $a < 0$ the expression will always be below the $x\text{-axis}.$Similarly, the solutions will be imaginary.
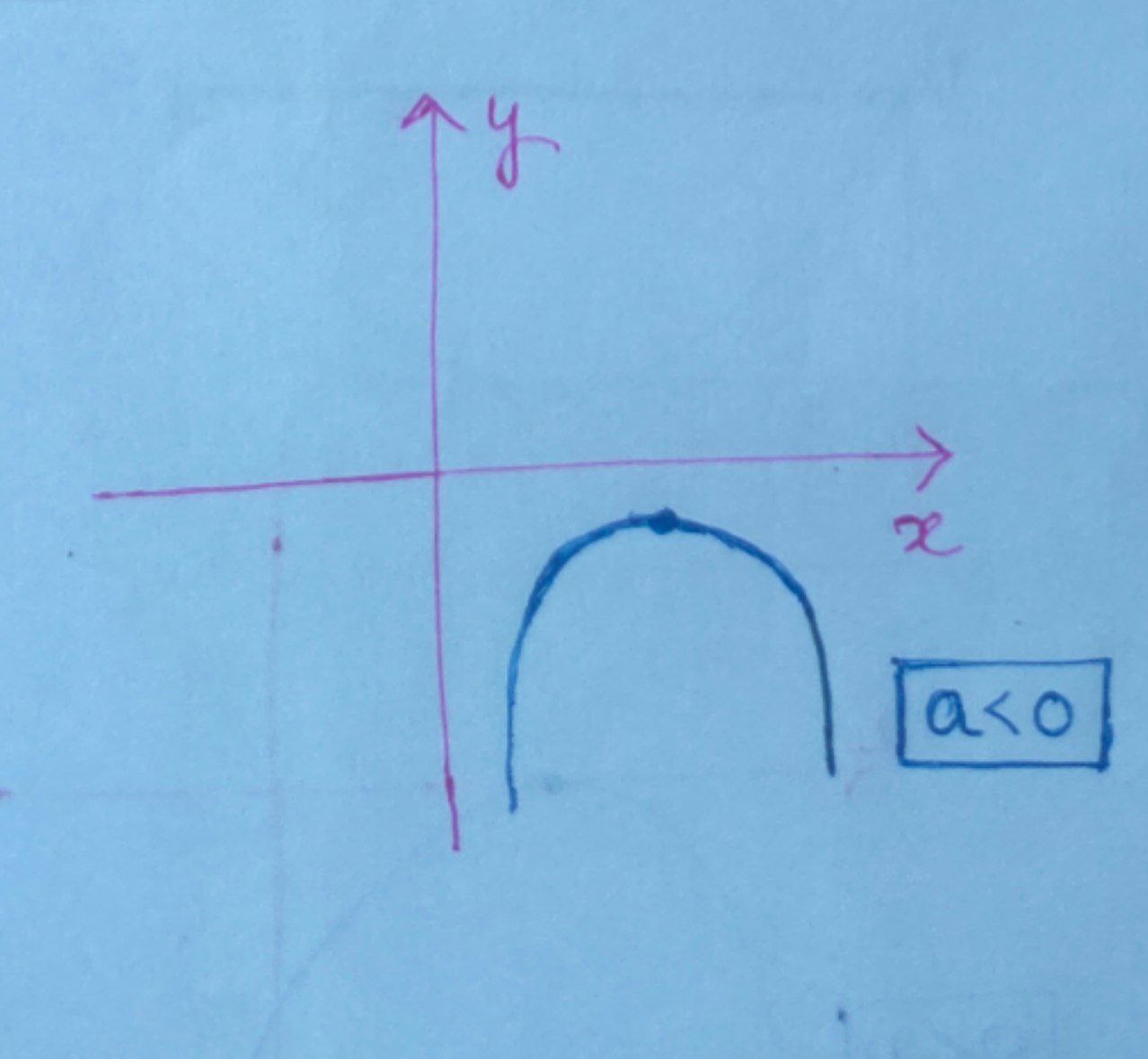
So, here discriminant $\boxed{D<0}$
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{b^{2} – 4ac} $
For the equation $(1),$ graph will be :
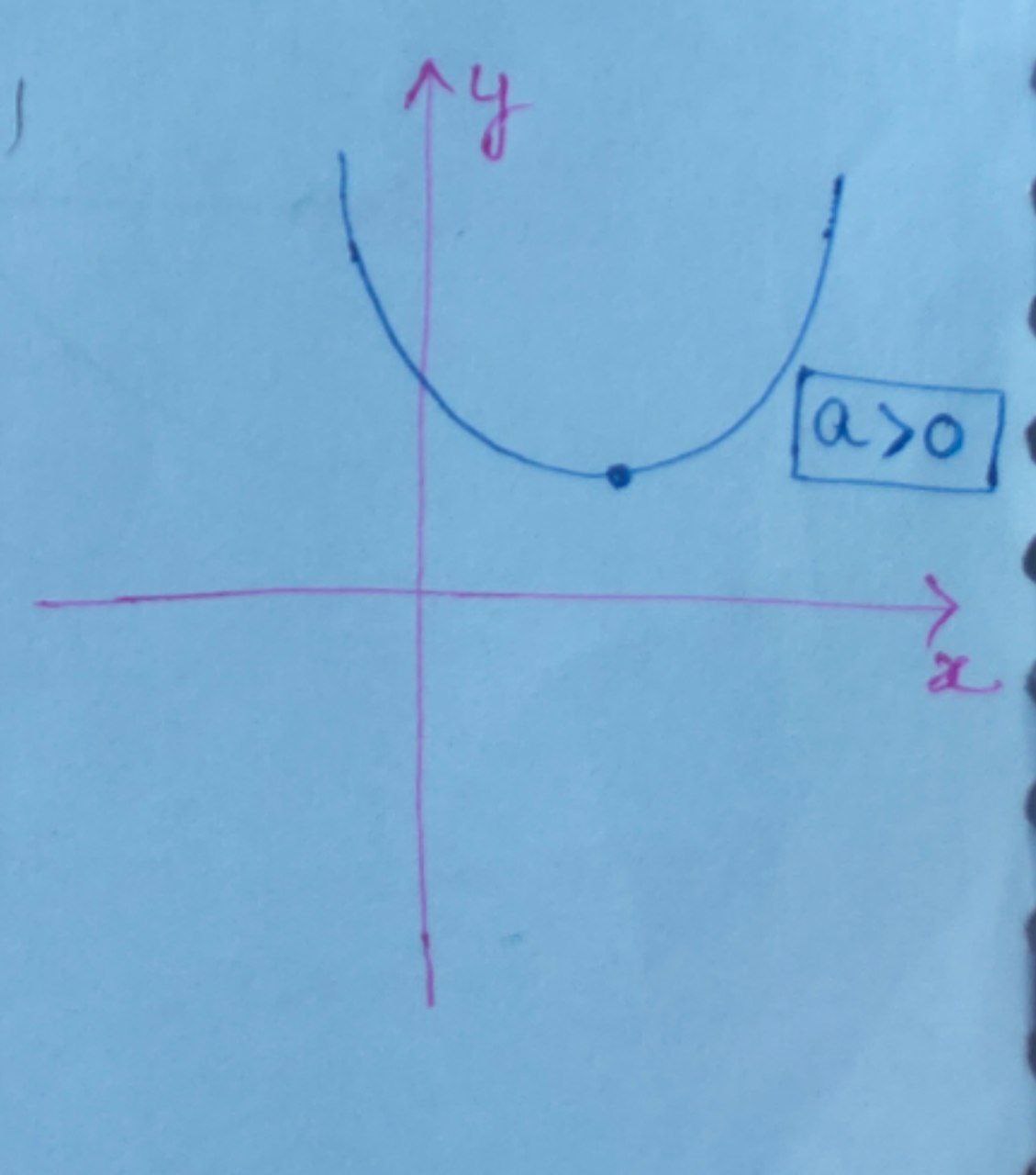
Here, $\boxed{\text{D}<0}$
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{ b^{2} – 4ac < 0} $
$ \Rightarrow (-a)^{2} – 4(2)(2) < 0 $
$ \Rightarrow a^{2} – 16 < 0 $
$ \Rightarrow a^{2} < 16 $
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{ -4 < a < 4} $
For the equation $(2),$ graph will be
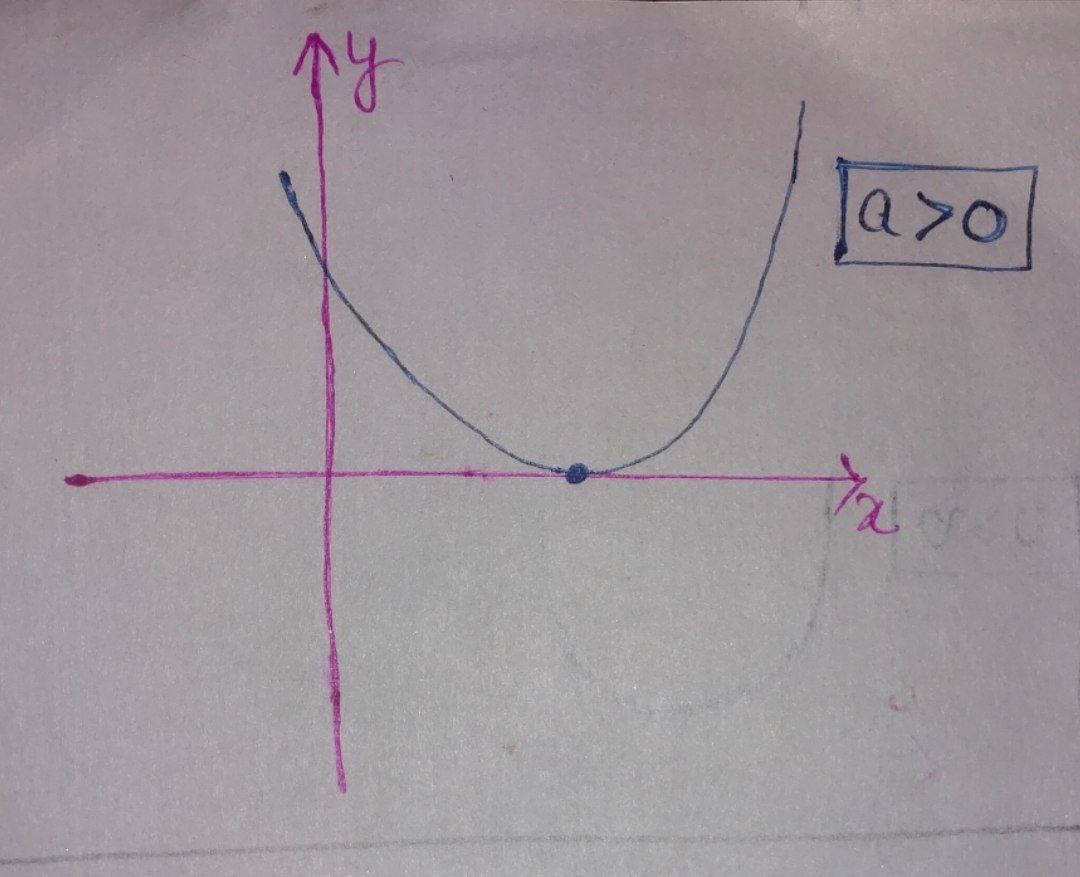
In this case, the graph can touch $x – \text{axis}$, so it can have at most one root.
Thus discriminant $\boxed{\text{D} \leqslant 0} $
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{ b^{2} – 4ac \leqslant 0}$
$ \Rightarrow (-b)^{2} – 4(1)(8) \leq 0$
$ \Rightarrow b^{2} – 32 \leq 0$
$ \Rightarrow b^{2} \leq 32 $
$ \Rightarrow b \leq \sqrt{32} $
$ \Rightarrow b \leq \sqrt{16 \times 2} $
$ \Rightarrow \boxed{-4\sqrt{2} \leqslant b \leqslant 4 \sqrt{2}} $
As $b$ is an integer.
So, $\boxed{ -5 \leqslant b \leqslant 5} $
For the largest value of $ 2a – 6b,$ we can take $a = 3,$ and $b = -5.$
$\therefore$ The largest possible value of $ 2a – 6b = 2(3) – 6(-5) = 6 + 30 = 36.$
Correct Answer $:36$
$\textbf{PS :}$ For equation $ax^{2} + bx + c = 0,$ expression $b^{2} – 4ac$ is called discriminant and denoted by $\text{D}.$
$\begin{array}{cl|l}\hline & \textbf{Value of discrimimant} & \textbf{Nature of roots}\\\hline 1. & D<0 & \text{Unequal and imaginary}\\ 2. & D = 0 & \text{Real and equal}\\ 3. & D>0, \;\text{and is a perfect square} & \text{Real, unequal, and rational}\\ 4. & D>0,\;\text{and not a perfect square} & \text{Real. unequal, and irrational}\\\hline \end{array}$
Reference: https://brilliant.org/wiki/jee-quadratic-roots/